
According to the US Department of Justice, over 7% of all US residents age 16 or older are victims of identity theft every year. Cyber hackers and criminals are on the prowl to steal personal data and use it for personal gain. Phishing and the use of malware are two of the many ways that hackers can access your personal information. This article points out some of these techniques and ways to combat them, including ways to strengthen your passwords to help prevent yourself from being a victim.
Hacking and Malware
Just like being in an unfamiliar part of town, being aware is the most important thing to remember when it comes to hackers and malicious software. Let’s start with looking at some the ways we are being attacked online:
Phishing is a technique used by online criminals to trick people into revealing information. Phishing and other forms of hacking are using social networks as an increasing source of illicit data.
Spearphishing attacks are targeted; criminals often glean personal information from social media sites including names of family members and friends in order to tailor their malicious phishing attack, or worse.
Malware or malicious software can be downloaded onto your computer or device via the internet and allow the hacker to take control of your computer. They may pose as downloads, attachments, emails, links to websites, or can be hidden in social media sites, and other platforms.
Keyloggers are hackers who use software to log every keystroke enabling them to obtain usernames and passwords typed on the computer. This is of great concern if the hackers have access to your computer over public Wi-Fi or a personal hotspot.
Protect yourself against hacking and malware
Be aware and:
- Examine emails you receive carefully before opening them, including their source and content. Do not open emails that look suspicious in any way.
- Know what type of antivirus software you have and evaluate any warnings that may pop up before clicking on them.
- Install current antivirus software, have up-to-date systems, proper browser security settings, and be generally aware of your surroundings.
Strong Passwords that are Easy to Remember
One of the greatest threats to both individuals and companies is the risk of getting hacked. This is why most company websites require many different types of characters when creating a password. However, it is incorrectly believed that to keep you safe from getting hacked, more complicated passwords are stronger passwords.
“Don’t confuse a difficult to remember password with having a strong password,” says Jacob Katzeff, a mathematics and computer science student at UCSC. Jacob pointed me to the following webcomic from xkcd.com, that illustrates the point of using multiple, random, but easy-to-remember words to form passwords that are very hard to hack.
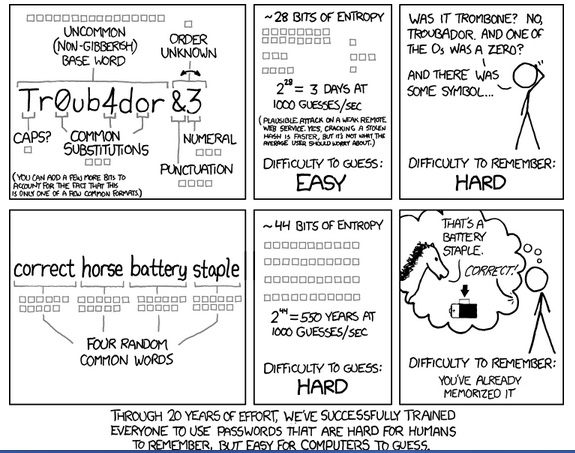
The best indicator of password strength is the length of the password. It makes sense that longer passwords take longer to hack than shorter passwords. It also makes sense to use common but random words to make strong passwords easy to remember. In the example above, using four random common works to create the password: correct horse battery staple is easy to remember but very hard to hack. (You can make it even stronger by adding uppercase letters and special characters). While the shorter, more complicated and harder to remember password: TrOub4dor&3 is easy to hack.
An easy method for creating stronger passwords is the technique of padding. Padding is when you add additional words, characters, or symbols to your existing password to increase its strength, without it being difficult to remember or type.
You can check the strength of your password on how secure is my password. It is free service sponsored by RoboForm, a password manager. Be aware that if you enter a password on a website it can be easily stolen. Be careful where you type your password and don’t share it.
Quiz – What is the most commonly hacked password?
123456 or password
Answer: 123456 (sadly there are many people who have not taken the time or used common sense to take the steps to protect themselves online)
Mobile Computing
We are living in a mobile society, so our smartphones and tablets go everywhere we do. Because of this, we need to make sure that our mobile devices are safe and secure so our information does not easily fall into the wrong hands.
To safeguard your mobile devices, remember to:
- Always password protect your device. What information do you carry in your mobile device? Would you be compromised if it were to be found or stolen?
- Encrypt your data. Don’t save passwords or other important information in your notes on your mobile device. Use a password keeper program that will keep them safe.
- Have the ability to remotely locate and wipe the device of data, if it is lost. There are apps such as Android Device Manager, Avast, or FindMyPhone which allow users to remotely wipe a device if it is lost.
Quiz – Which mobile operating system has the strongest inherent security? iOS or Android?
Answer: iOS, but Android is closing the gap. iOS apps are only available from iTunes which is screened by Apple for malware.
Public Wi-Fi
Free Wi-Fi at places like Starbucks are convenient, but you may be putting yourself and your computer at risk. Wi-Fi hotspots are generally unsecured networks which hackers tend to exploit.Here are 6 tips from CNET about the safe use of public Wi-Fi hotspots.
- Be aware that you’re never secure. It is not difficult for a hacker to tap into your activity and get your personal information. Even if a hotspot requires a password or guides you through a log-in screen, you’re still at risk.
- Utilize built-in security tools. Investigate the built-in security features of your device…enable your firewall and check off “Block all incoming traffic,” etc.
- Protect your passwords. Hackers can retrieve saved passwords from your registry or install keyloggers, which make your keyboard activity available to them
- Look for the padlock in the URL address bar. Some websites use HTTPS://, where advanced encryption is provided to protect your activity.
- Check the network name carefully. Hackers might set up fake networks like “FREE Public Wi-Fi” or “Starbucks FREE.” It is advisable to check with the employees where public Wi-Fi is offered to confirm the name of their network.
- Use common sense. Treat all networks as a security risk. Don’t do any banking, online shopping, or other activities that would expose your private information when using public Wi-Fi.
Of course, the best solution is to not use public Wi-Fi at all. Instead, learn how to use your phone as a personal hotspot.
Quiz – True or False? If we use a well-known/highly regarded email vendor our internal emails are safe. (e.g. From one g-mail user to another)Answer: True. Almost all email vendors employ SSL encryption that protects emails to and from the email server. Internal emails do not travel unprotected over the internet.
Final Thoughts
In summary, identity theft is one of the fastest growing crimes and we need to do everything we can to keep our private information safe and secure. Make sure to use padding and longer, random but easy to remember words (with uppercase and special characters), to create passwords that make it more difficult for hackers to crack. When using your mobile devices, password protect any data stored on that device, encrypt and have the ability to remotely locate and wipe the device if it is lost. If you use public Wi-Fi hotspots, make sure to take all the common sense safety precautions listed above.




Leave A Comment